-
How to use visual fault locator
In the optical fiber network wiring, in order to adapt to the environment and various requirements, usually needs wire, welding. Fiber is fragile and prone to failure, Therefore, optical fiber detection tool has become a common tool in integrated network routing.
As one of the commonly used optical fiber detection tools for troubleshooting network faults, optical fiber visual fault locator can quickly detect optical fiber connectivity and fault points. So do you really know about visual fault locator? What other uses it has besides detecting fault points? How does it work?
What are the uses of visual fault locator?
It’s mainly used for detecting broken point. The principle:The 650nm semiconductor laser is used as the luminescent device, which emits stable red light through constant current source drive, and connects to the optical interface to enter the optical fiber, to realize the optical fiber faul
-
6 notes you must know after FTTH
Fiber to the x (FTTX; also spelled "Fibre") or fiber in the loop is a generic term for any broadband network architecture using optical fiber to provide all or part of the local loop used for last mile telecommunications. As fiber optic cables are able to carry much more data than copper cables, especially over long distances, copper telephone networks built in the 20th century are being replaced by fiber.Today we are going to talk about the matters needing attention after FTTH
-
Some knowledge about fiber parameters
Given the great popularity of optical communication lines in the past few years, most of them are currently based on modern single-mode fibers. However, both singlemode and multimode fibers come in many types and categories that conform to established standards and factory specifications. The article "Multimode and Singlemode Fiber Optic Cables" raises the main issues related to the difference between these types of optical fibers.
The specifications for the various types and categories of fibers are contained in developed international standards. In addition, numerous factory standards and specifications are used in local markets.
Terminology and classification
International Electrotechnical Commission Technical Committee 86 (IEC TC86) is responsible for international standardization in the field of fiber optic communications, which defined the following types of types: Multimode fibers, e.g. A1a, A1b, A1d ..., further di
-
What is Wi-Fi 6 and what are its benefits
Since the announcement of Wi-Fi 6 in 2018, the standard has been rife with rumors and speculation. Almost two years have passed since then, and although the standard has not yet been finally approved, the first devices with its support have already appeared on the market. And now you can try to understand what this Wi-Fi 6 is, and how we managed to miss the five previous ones.

Why Wi-Fi 6?
Because the Wi-Fi consortium decided so. Now, new versions of the IEEE 802.11 wireless data transfer protocol will be designated not by incomprehensible numbers and letters, but simply by a serial number. Wi-Fi 6 is 802.11ax, and previous versions, starting with the original 802.11 introduced in 1997, received numbers from 1 to 5. First, it's easier and more understandable, and secondly, the consortium promises that soon future generation number (starting with Wi-
-
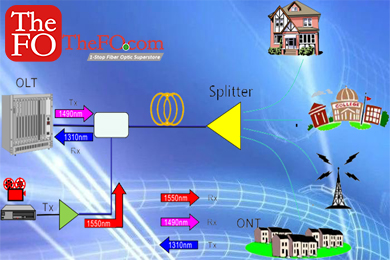
OLT equipment introduction
1. OLT basic concept
OLT (Optical Line Terminal) optical line terminal, PON network consists of OLT, ODN and ONU. The OLT belongs to the service node side device of the access network, and is connected to the corresponding service node device through the SNI interface to complete the access service of the access network.
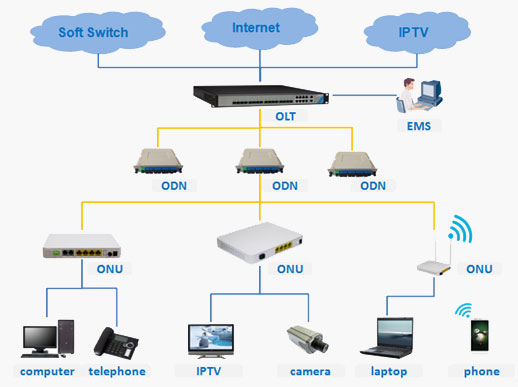
In the PON technology application, the OLT device is an important central office device, and its functions are as follows: 1. The front-end (aggregation layer) switch is connected by a network cable, converted into an optical signal, and interconnected by a single optical fiber and a splitter at the user end.
1) Realize the functions of control, management and ranging of the ONU of the user equipment. 3. The OLT device is the same as the ONU device.
The OLT is connected to the central office equipment. If the optical signal is too strong (som
-
Precautions and daily maintenance of optical fiber fusion splicing
Frequently noticed problems during operation
1. Clean, the inside and outside of the fiber fusion splicer, the fiber itself, the important parts are the V-groove, fiber presser foot and reflective lens.
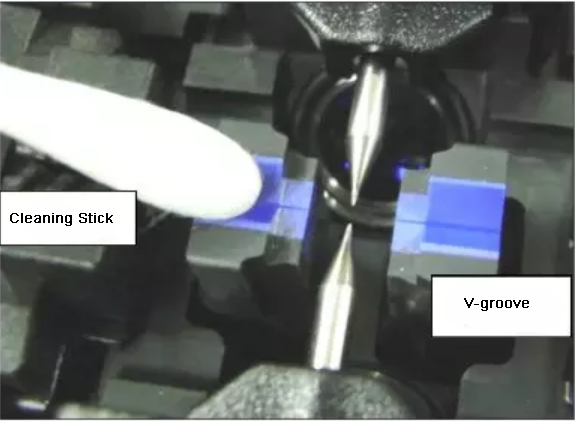
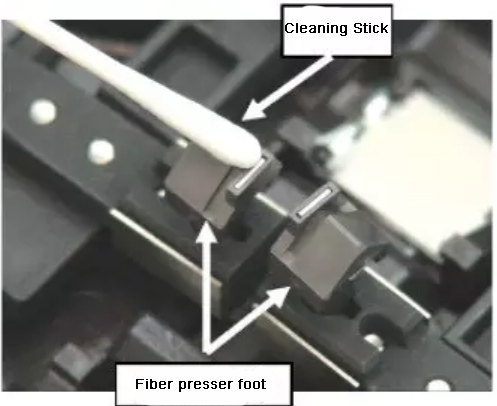
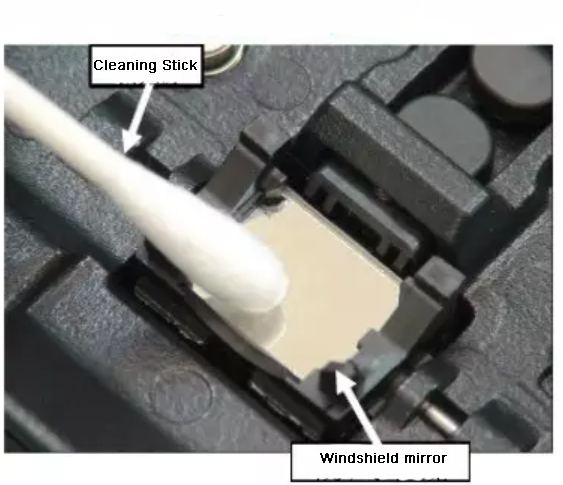
2. When cutting, ensure that the cutting end face is 89°±1°, which is approximately vertical. During the process of placing the cut optical fiber at the specified position, the end face of the optical fiber should not touch any place. If it encounters it, we need to clean and cut again: emphasize Clean first and then cut!
3. When placing the fiber in its position, don't be too far or too close, 1/2 place, proficiency!
4.
-
6 Steps for fiber fusion splicing
Welding process
1.Tool
Fusion Splicer, cutting knife, optical fiber, wire stripper, alcohol (99% industrial alcohol), cotton, heat shrinkable tubing.

2. Discharge experiment
1) Purpose: to adapt the optical fiber fusion splicer to the current environment
2) Reason: better adapt to the environment, more adequate discharge, better welding effect
3)Specific methods:
(1) Add fiber and select the "discharge experiment" function. The screen shows the discharge intensity until "discharge 0K!" appears.
(2) Empty discharge, press the ARC button
The number of discharges: "The discharge is too strong, the discharge is too weak" will appear in the process, until the discharge is OK.
Discharge time:
- W
-
Talking about 5g positioning technology
From 2G to 4G, the positioning technologies of cellular networks mainly include: E-CID, AoA, ToA, TDOA, etc.
More details please add official account: whatsapp/ skype +8613625297051
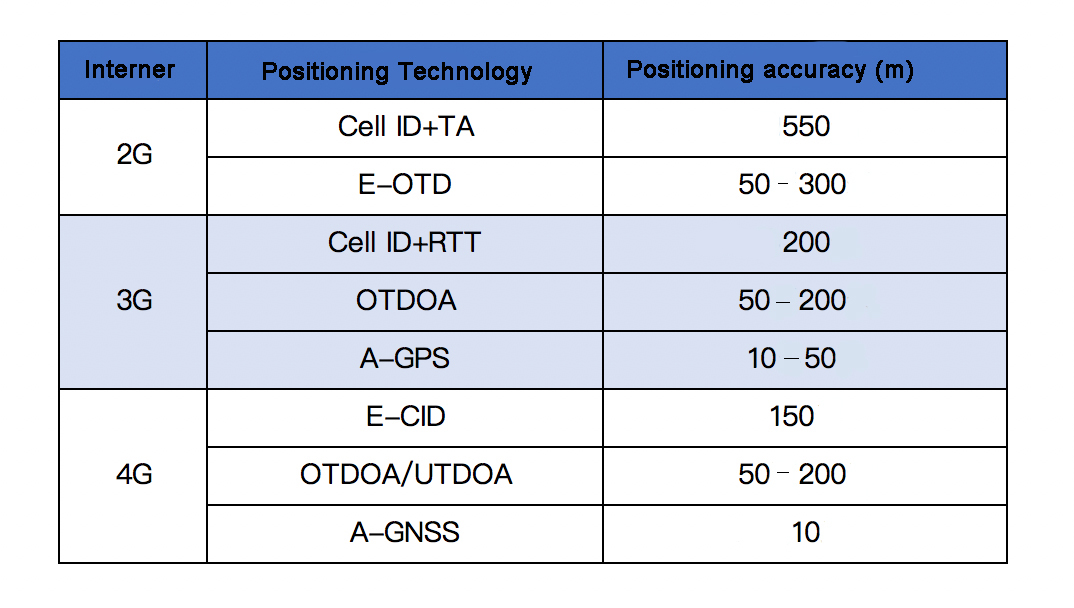
Today, let’s talk about how the positioning technology in the 5G era is realized.
Positioning needs in the 5G era5G will enable diversified applications in all walks of life. A large number of application scenarios such as the Internet of Vehicles, autonomous driving, smart manufacturing, smart logistics, drones, and asset tracking have higher requirements for positioning capabilities, such as vehicle formation in the Internet of Vehicles, Active collision avoidance requires a positioning accuracy of up to 30 cm, and a positioning capability that supports high-speed movement and ultra-low delay; remote control of drones requires 10-50 cm. A