-
Fiber costs: why fibre is getting more expensive in South Africa
Categories: OthersAt the beginning of 2020, several of South Africa’s top fibre network operators warned Internet service providers that they essentially planned to increase wholesale prices. With retail price hikes happening on four of South Africa’s major fibre network operators, consumers are asking why the price of broadband is increasing.
Inflation, labour, and foreign exchange
“The reality is that our costs are increasing on an annual basis in line with labour costs of constructing networks, and inflationary increases in materials and other costs,” Frogfoot CEO and founder Abraham van der Merwe said.
“None of these factors even take into account the massive weakening of the rand, which substantially increases our material costs as most is imported.”
Fibre networks aren’t considering the increased costs as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and resulting lockdown,as they will simply absorb those and not try and recoup any of these losses fro
-
What is a curve?- How is the graph formed?
Categories: OTDRFirst of all, what is a curve? just look at the picture!

The red box in the figure above is a common curve chart in daily life.
How is the graph formed?
After the OTDR emits the test light, the circuit diagram is constructed through the principle of back-to-back Rayleigh scattering and Fresnel reflection.
Backscatter
The uneven deposits and impurities distributed along the fiber core scatter the test light back to the OTDR through the principle of scattering.
-
WHAT DOES A FIBER CLEAVER DO?-TheFO.com
When we need to join two optical fibers together, we usually use mechanical splice or fusion splice.
The quality of a cleaver is determined by the following statistical parameters: how smooth the cleave is, how the angle of the cleavage surface is
different from 90°, how often the cleaver breaks fibers, how convenient it is to work with it, what the cleaver’s capacity is, etc.
Both optical fiber slicing techniques require that the fibertips are a smooth end face that is perpendicular (90°) to the fiber axis as shown below.
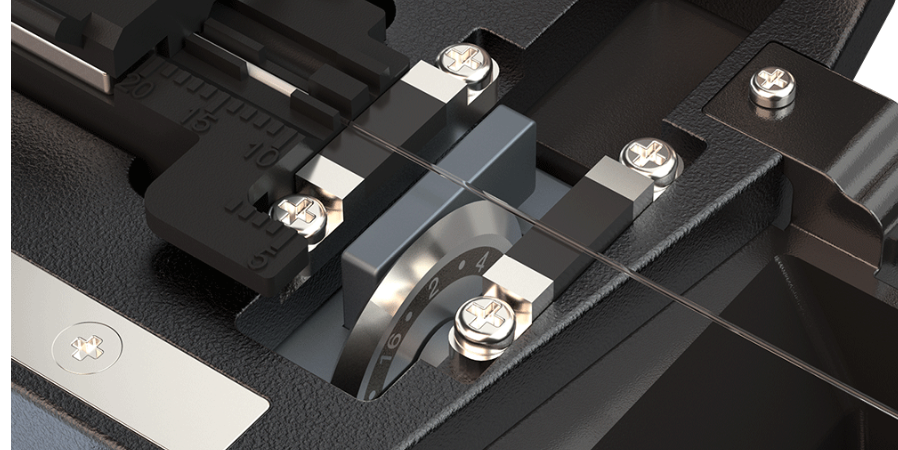

In the cleaving process, the brittle gla
-
Fusion Splice vs Mechanical Splice Which one to choose?
Fusion Splice vs. Mechanical Splice
Both fusion and mechanical splicing do the same thing - they connect the two fibers together and keep it in such a way that the light signals can be connected. In more detail, fusion is the point of attachment of two or more fibers that are fused together. This is achieved by a machine called a fusion splicer that performs two basic functions: aligning the fibers and melting them together, usually using an electric arc.
The mechanical splice is a simple alignment device that does not permanently connect the two fibers together and is designed to hold the ends of the two fibers in precise alignment so that light can pass from one fiber to another Root fiber.
Fusion stitching and mechanical stitching involve four basic steps. For the two methods, the first two steps are almost the same, and the last two steps are a little different.
Steps for Fusion Splice
Step